
As one of the world’s leading typeface designers, and this year’s 99U Alva Award winner, Tobias Frere-Jones believes that the best way to learn a new skill is to “break things down deliberately” to understand how it’s really done.
In this talk, we learn to see the beauty in taking risks. Frere-Jones explains that in order to do our best creative work, we must not just permit moments of confusion, but actually go chase them. “When trying to figure out a problem, pause for minute, and see if you can make it worse,” he says. “A structure can really describe itself as it falls apart.”
Over the past 25 years, Tobias Frere-Jones has created some of the most widely-used typefaces, including Interstate, Poynter Oldstyle, Whitney, Gotham, Surveyor, Tungsten, and Retina.
Tobias received a BFA in Graphic Design from the Rhode Island School of Design in 1992. He joined the faculty of the Yale University School of Art in 1996 and has lectured throughout the United States, Europe, and Australia. His work is in the permanent collections of the Victoria & Albert Museum in London and the Museum of Modern Art in New York. In 2006, The Royal Academy of Visual Arts in The Hague awarded him the Gerrit Noordzij Prijs for his contributions to typographic design, writing, and education. In 2013 he received the AIGA Medal in recognition of exceptional achievements in the field of design.
As a typeface designer, I get a lot of questions about– about the work that I do. When I describe what– what I do for a living, this can be one of the responses. [LAUGHTER] And taken a little further, you’ll get to the– sort of the classic question that typefaces– that every typeface designer gets, which is why make more typefaces? Aren’t there enough already? And I used to hate this question, because it always sounded like someone saying to me, like, you exist? But what’s up with that? [LAUGHTER] But– but I actually welcome this question now, because it’s an opportunity to explain what I do and advocate for its value. And I think it’s also– I think it’s also a powerful thing to present the mission statement of your career, as we say it out loud, in your own voice, to hear yourself saying that. It sort of helps keep you grounded that way.
But as I think of it, typeface design stands at this curious intersection of culture, and language, and technology. And any one of these can present a new problem or a new challenge. But certainly, when they start combining with each other, then there will be new problems to confront with culture, and technology, or technology and language. These can turn into problems to solve.
So while typeface designs can be artistic expressions, and they can be cultural artifacts, if they are fully realized and properly executed, they’ll be the solution to a problem. That’s how I think of it. And I think that’s– that makes it more interesting, I think. Also, it makes it more difficult, but thankfully, I have an affection for things that are difficult. So typefaces are solutions. And we need them, because we keep having new problems. So that’s how I’ve come to– come to think about it. How I’ve– that’s my answer for that– that perennial question. So it means that I spend– I spend a lot of time thinking about where I’ll find these answers for whatever challenge is at hand, and then figure out how to turn that answer into Serifs and Excites, and Bolds, and the rest of all that. So to– so to understand the– sort of the way I go about this, I’ll have to go back to my sort of previous life as a painter.
This is what I used to do before I was– I was a typeface designer. And in the way that I approached painting, questions and answers exist independently of each other. They don’t rely on one another. It’s possible to find an answer before you actually know what the question is. And in the kind of painting that I did, there was no explicit problem to solve. There just was sort of the generalized challenge of creating an atmosphere, or taking some state of mind and– and making that visible. But that idea of finding the answers before you know what the questions are, I’ve always– it’s something that I found really valuable, and something that I’ve kept with me, as I moved into type design, and it’s– it’s implication is that you have to collect everything– ideas, objects, anecdotes– and trust that these things will be useful at some point, if not today, then perhaps tomorrow. It also means that you will probably end up with a storage space full of junk. [LAUGHTER] Actually, I have two, come to think of it. But you become a kind of pack rat. And I don’t know. That’s– that’s– you’ll see how this– what this turns into.
While I was at college, I had decided that type design was the field that I would go into, but discovered that there was no organized instruction in this particular field. So I had to– it was up to me to work this out for myself. And the process of reading is a really complicated one, if you think about this for a moment. If I– I can make a set of marks and declare that each one of these has some phonetic value, then pass them on to someone else who will organize them into some sequence, these things will get passed onto someone else who will unpack these forms, hopefully agree with the declaration that I’ve made, and receive the content of some third party, hopefully, without any kind of distortion along the way. This is a really complicated process. And I thought that if I aspire to shape some part of this process, I really ought to know how each part of this– this string, this contraption, works.
So how I am I going to do that if I’m not really getting any help and I’m on my own here? So I devised a sort of plan for self education. It’s something I sort of instinctively done for years. And in this case, my plan centered on breaking stuff. I was absolutely the kid who would take the– the radio, or the alarm clock, and take it apart and see how it works. I liked to have the batteries in and the whole thing turned on while I was doing it, so that I could find out when the radio would go silent, when I pulled out this wire, or undid this bolt, because that’s how I would learn something. That’s where sort of the real lesson would come from. And I’ve always thought that there is something really informative in watching something break or collapse, that a structure can be– can describe itself really eloquently as it falls apart.
So if I wanted to learn about reading, what would happen if I tried breaking this process in some way?
So on my own I created a series of typefaces that had the explicit aim of throwing wrenches into the works of the process of reading, very deliberately and with a specific target to see how exactly things would screw up. One would focus on taking some central assumption about how text is meant to work, like one letter ends before the next one begins. What happens if that’s not the case? What happens if you pull that bolt out? Will things keep working? Another focused on the idea of ingredients and recipe. So what would happen if you had all of the things that you need to recognize these letters accurately, but then did a little bit of rearrangement? What would happen?
As it turns out, it kind of messes with your head, at least it messed with my head. But there is one experiment that began when a couple friends of mine mailed me a flyer that– that someone had handed them on the street. This is not it. It’s– it’s lost, or it’s buried in some storage space somewhere. But it looked roughly like this. And they sent it to me with this sort of joking dare to try to make a typeface out of this– this blobby mess of a thing. And I actually took it seriously, because I saw on this a really great way to break the alphabet. This is one I hadn’t thought of before. So I made a typeface called Chain Letter out of this– this photocopied flyer that had been copied over and over again. And what I– I thought it was fascinating is at the shapes had become so distorted, that the very identity of them were starting to fade as well. So this is the Aegean Sea, cap G and cap C.
But there’s barely a line between these two shapes now, because so many things have decayed and fallen away. There is a tiny bit of a hint of a crossbar, or I should say, a tiny hint of something, which might be interpreted as a crossbar, in which case you can conclude that this says hi. Or you could skip over that and conclude this is the Roman numeral three. What would happen with that kind of ambiguity? Would our experience as readers be able to step in and figure out, that this is an m with a whole in it, or that these are just two shapes that have nothing to do with each other? Later I took this idea a little bit further and started making some– some pen and ink sketches, in this deliberately sort of sprawling, sloppy style, being deliberately vague about the letters that I was drawing. And the– the endpoint for this was this typeface called Sum of the Parts. And the challenge here, or the goal here, sometimes I’m tempted to call it the sort of the punchline, is that there appear to be 26 letters here. But they’re actually only 11. And each one serves to represent at least two, sometimes three other letters of the alphabet.
So– and the question here would be what– how much could context and experience– how much slack could those pull up if the individuality of each letter has been completely shut down?
And it turns out– they can pull up some of the slack, not completely, but it’s still an important lesson to– to think about. But throughout all this, I was just collecting answers, just wagering that at some point in the future I would find some question that looked sort of like this, and be able to apply it. So even the ones that– the experiments that– that blew up, became completely illegible, like this one. They were informative in their own particular way. The lesson here is don’t do this. [LAUGHTER] It doesn’t work. But it was still valuable. I wasn’t getting paid. I wasn’t– I was out of school by this point. I wasn’t getting college credit for any of this stuff. But this still– you know– I was still acting like a pack rat, collecting all the stuff and saving it somewhere.
So if we fast forward several years, and I’m all grown up, or at least I present reasonably well as a grown up, and I’ve got clients. “The Wall Street Journal” was getting redesigned, top to bottom. And with their external consultants, they decided that the stock listings section of the newspaper needed to be redone. The whole thing needed to be pulled apart and put back together again. And they needed a new typeface for their stock listings. Now the newspapers are a hostile environment for typography, for all kinds of– for physical reasons and operational reasons. Because the paper is cheap. The ink tends to be kind of thin. The press is moving really fast. Space is literally at a premium. So everything is working against clarity and beauty. But on the stock page, I realized that it actually gets even worse, because the content there isn’t even language. [LAUGHTER] This is what the stock– this is the kind of stuff you’ll find on a stock page. And normally, if you’re reading a story anywhere else in the paper, and one letter is a bit vague, so a bit of ink smear, your experience as a reader can fill that in, and sort of your experience and can step in as a judge and resolve the ambiguity. That’s not going to work here. Because any sequence of letters and numbers, cap and lowercase, any of this isn’t going to look plausible. So your experience is not really going to help you out here.
So I thought that something kind of radical was needed in the face of such a tall order. And at this point, I remembered a– an anecdote, one of these things I had collected and stored away somewhere. And it was about– it was about a filmmaker from years past. And in his class, at whatever university it was, he liked to show his students really lousy films as well as really good ones. And the idea, as I understood it, was that if you just look at really good work, you’ll learn how to make good films, but only in the way that that person had done it. If you look at work– at work that’s crap, and talk about how it went wrong, and what else could have been done, you get the same kind of knowledge, but without that sort of built in preference. You get the insight without the bias. And I thought it was a really fascinating idea. It stuck in my head for a really long time. I believe the filmmaker was Fritz Lang, though I was– I haven’t been able to confirm that. It’s possible I’m getting that wrong. It’s also possible that I just made the entire thing up. But either way, it– this seemed like an idea worth remembering and considering. This came to mind again while I was thinking about what “The Wall Street Journal” needed, and this very severe problem they had, and realized that in this– this idea of what I was thinking of as the inverted negative, I already had half of this work done from way back when in my, you know, just barely out of adolescent years, when I’d stay up late at night figuring out ways to break the alphabet. I had a kind of reverse blueprint of how to take on this really serious problem of legibility and environment.
So what would happen if I took those old experiments, like Chain Letter, and Sum of the Parts, and turn them upside down, and did the exact opposite of what I did there? What would happen? So what I came out with in this design, that ended up being called Retina, I created a strategy where every– I identify in every letter a feature that happens there and nowhere else. And so in the case of the capital B, I decided that was the triangular white space on the right exterior where the two curves meet. So that part of– of the shape, is blown up as big as possible, and the rest of the letter just follows along however it needs to. And following on– on the sort of the Sum of the Parts model and turning it upside down, where there are shapes that had a kind of structural sympathy with one another, they were pushed as far away from each other as possible. So the profile of the E is sort of vertical as I can get it. And the profile of the F is diagonal as possible. All this had to– had to get added up with these big chunky notches taken out of intersections, to accommodate and sort of to anticipate, the ink spread that would happen on press. So– so this is what– what this turned into in the end, a much larger family, but this is one– the sort of core of what Retina looks like. This is one of the most satisfying projects I’ve ever done. I meant to say that before. But one of the really fun parts of this was subjecting these forms to various forms of duress.
Trying to break this, and seeing what happens, and putting it side by side with Helvetica Light Condensed, which is what the “Journal” had been using before, and trying to see what would happen if someone’s vision were not quite up to– you know– were not quite 20/20, which as it turns out, is actually the prime readership of the stock page– [LAUGHTER] –of the Journal. Because the people who were doing this professionally are getting their quotes online. The only people who are getting their stock prices out of the paper are retirees. So it actually got worse. But it was amazing to see how fragile Helvetica can be. I will resist the temptation to go off on this rant about Helvetica. It does not deserve the reputation that it has, whatever. I’m not going there. Don’t worry about it. [LAUGHTER]
But a– a large part of– or this– potential for confusion between shapes was particularly urgent with the numbers. Because this forms a– you know– something like half of the content of a stock page, and there were four numbers in Helvetica. And the 3, the 6, the 8 and the 9 that are just one smudge away from being mistaken for one another. And again, we’re not going to be able to rely on our experience in our content to figure out that something’s wrong. So the numbers in the Retina push all these shapes as far away from each other as possible, so that they are as durable as possible, and as immovable as– if I could ever make them that way. So in the end, the paper was able to get 11% more text on the page. And I did the math about the– you know– how much paper “The Wall Street Journal” was saving, and you know, how many issues in a day, how many copies in a year, and how many trees that added up to. And I felt pretty great about myself, but then discovered that the paper was using that opportunity to just sell more ad space. [LAUGHTER] So I don’t know. I did my part. But– but the best part– the best comment about this design came out of one of the focus groups, where a retired stockbroker, someone who’s 80 years old, looked at this new format for the paper and said, I don’t know what you did, but I don’t need my glasses anymore to read the prices in the paper. It was one of the best things I’ve ever heard about anything I’ve ever done. But the– so the theme through all of this– that we’ve been talking about– is self- education. And it’s always been an important part of my life whether I’ve realized it or not.
And if I have any advice to offer, it’s to not just– you know– permit these moments of disorientation, or confusion. But actually go chase them. If you’re trying to figure out how to solve a problem, pause for a moment and think about how you can make it worse. Try to break this thing. And then walk into that tremendous mess that you’ve made, and with all of your senses on, all of your imagination turned up. Because you can find something pretty amazing in all that mess, in all that wreckage.
Thank you.
from 99U99U http://99u.com/videos/53989/tobias-frere-jones-break-things-deliberately/
 https://medium.com/swlh/mediums-best-design-writing-of-2016-68de5ed2b7d9
https://medium.com/swlh/mediums-best-design-writing-of-2016-68de5ed2b7d9




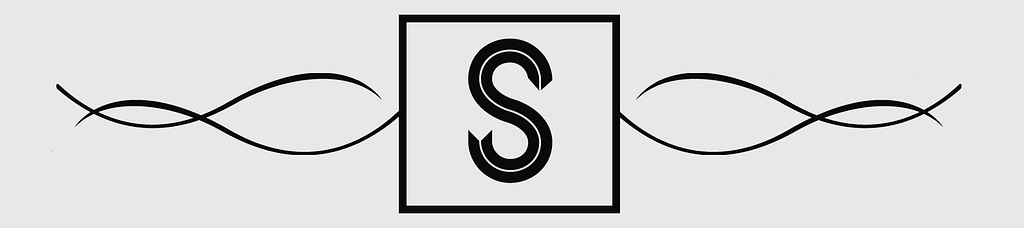

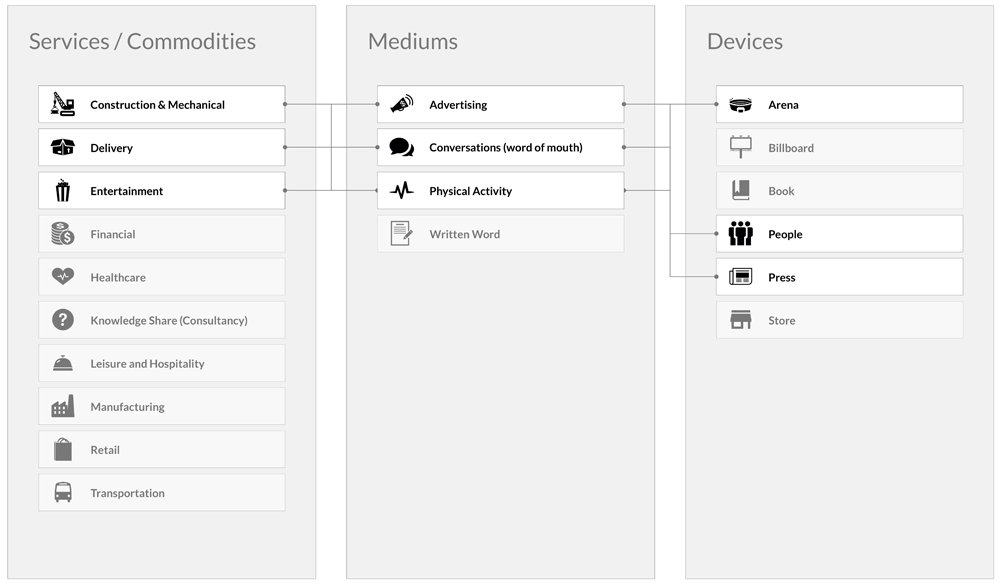

/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/7840969/Screen_Shot_2017_01_20_at_8.59.08_AM.png)




